Knowing your target audience is one of the most crucial elements of a successful marketing strategy. Discovering their habits, behavior, and most prominent painful points helps businesses to sell their products/services to them successfully.
This article will explore nine crucial psychology concepts for marketing, shedding light on how marketers can leverage these principles to create compelling campaigns and adapt strategies based on the way people make decisions.
What is Marketing Psychology?
Marketing psychology, which is also called ‘Neuromarketing’, applies neuropsychology to content, marketing, and sales to influence and boost purchasing decisions.
The brain works uniquely and creates shortcuts to help people make decisions. If you can take advantage of understanding these shortcuts, you’ll be able to better expand your audience. In short, understanding the how and why of how people think and act allows you to improve your marketing campaigns. In addition, this insight can help you develop a stronger brand identity.
There are several methods to apply marketing psychology, including:
- Resonating with your target audience by using special emotional trigger words.
- Applying psychology principles to content writing.
- Choosing website colors based on how they are perceived by visitors (more on color psychology here).
Why Psychology Is So Important In Marketing?
Understanding the thought processes of your target customers is an essential step in marketing. By understanding their likes, dislikes, wants, and desires, you can gain a well-rounded, realistic idea of what type of marketing messages will resonate.
Psychology gives you key insights into human behavior
Marketing strategies and tactics are changing. Just a decade ago, no one was thinking about how to increase engagement on YouTube and TikTok. But human psychology never changes. Look back through history and we see the same patterns repeated, the same problems and solutions, almost endlessly. In many instances, our behavior is predictable.
Psychology helps you elicit emotional responses from your target audience
Effective marketing requires both the emotional and cognitive needs of the target audience. A knowledge of psychological principles will help you to understand what makes you feel something. This is crucial for sales and also for receiving brand-loyal clients, who will promote your product or service for free.
Psychology helps you overcome fear, uncertainty, and doubt
Marketers can use fear, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD for short) to cause a pattern interrupt in their audience, making them stop and change their behavior.
By learning psychological techniques you can use your FUD as a weapon when it makes sense, and offer a benefit to your customers.
Important Principles of Marketing You Should Know
Psychology is behind all human behavior. It only makes sense that, whether we consciously realize it or not, psychology also drives our consumer decisions. As a result, marketers can strategically take advantage of psychology to encourage the decisions they want.
To help you create more engaging and effective marketing campaigns, here are the common 9 principles and theories of marketing psychology:
Halo Effect
The Halo Effect, a cognitive bias, occurs when people’s overall impression of a person, brand, or product influences their feelings or thoughts about specific traits or qualities.
In marketing, creating a positive and memorable overall impression can have a profound impact on consumer perception. Brands often use celebrity endorsements or showcase positive associations to invoke the Halo Effect.
For example, the Halo Effect shows that we tend to see the well-packaged product as more valuable, even if the other might be superior. This is because the positive perception of the packaging forms our overall opinion of the whole product, impacting how we estimate its overall quality.

Loss Aversion
Loss aversion means that people are afraid to lose over acquiring equivalent gains. In marketing, emphasizing potential losses rather than gains can drive action.
How can you leverage this psychological trait in your marketing strategy? Let’s see:
- Sense of urgency: Add the limited-time offers and prompt them to act fast.
- Fear of missing out: Point out the losses according to their pain points. Exclusive deals and fear-of-missing-out tactics capitalize on this psychological concept. Compel consumers to make decisions to avoid perceived losses.
- Ownership: Show them they already own your products/services and prompt them to retain them.
- Scarcity: Explain to them that they’ll receive something very rare or special.

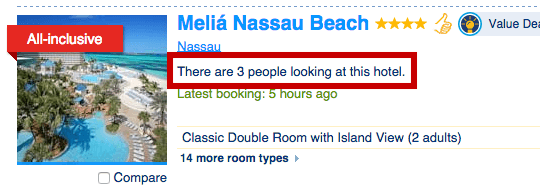
Social Proof
Social Proof is the phenomenon where individuals follow the actions of others, assuming that those actions reflect the correct behavior. In marketing, testimonials, user reviews, and social media influencers are potent tools to harness social proof. Consumers are more likely to trust a product or service if they see others approving it.
Start collecting reviews, case studies, and testimonials from satisfied customers and show them to the prospects. Share them inside your website, also, in a dedicated section where people can learn what others believe about you, social media accounts, and special review platforms.

Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for, interpret, and remember information that confirms pre-existing beliefs. In marketing, this can be harnessed by aligning brand messages with consumers’ existing beliefs.
Marketers should be mindful of the information they present and ensure it resonates with the target audience’s existing perspectives.

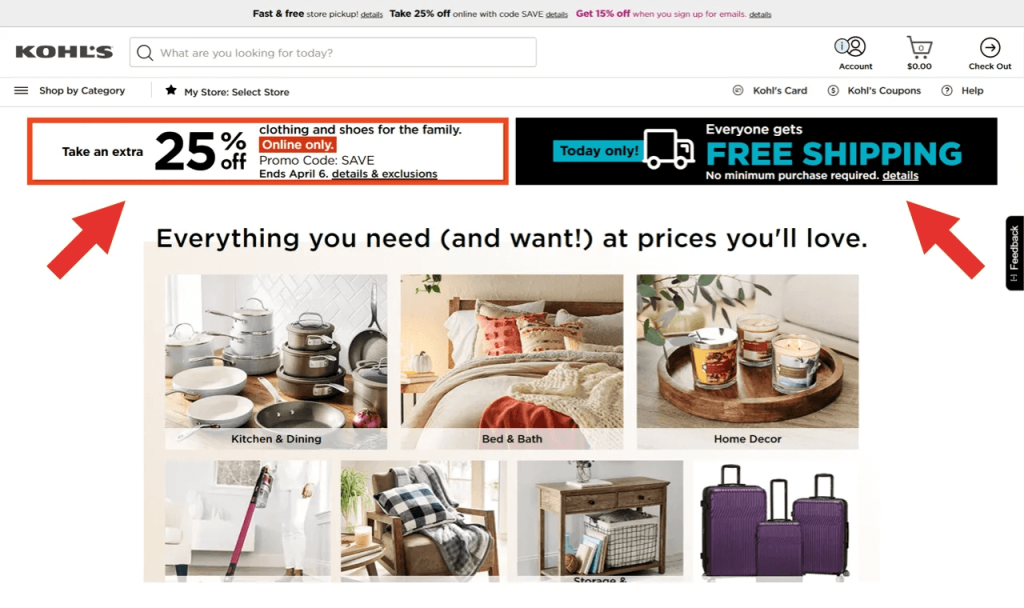
Scarcity Effect
The Scarcity Effect exploits the principle that people value things more when they perceive them as scarce. Limited editions, exclusive releases, and countdowns all tap into the scarcity effect, compelling consumers to act quickly before a product or opportunity becomes unavailable.
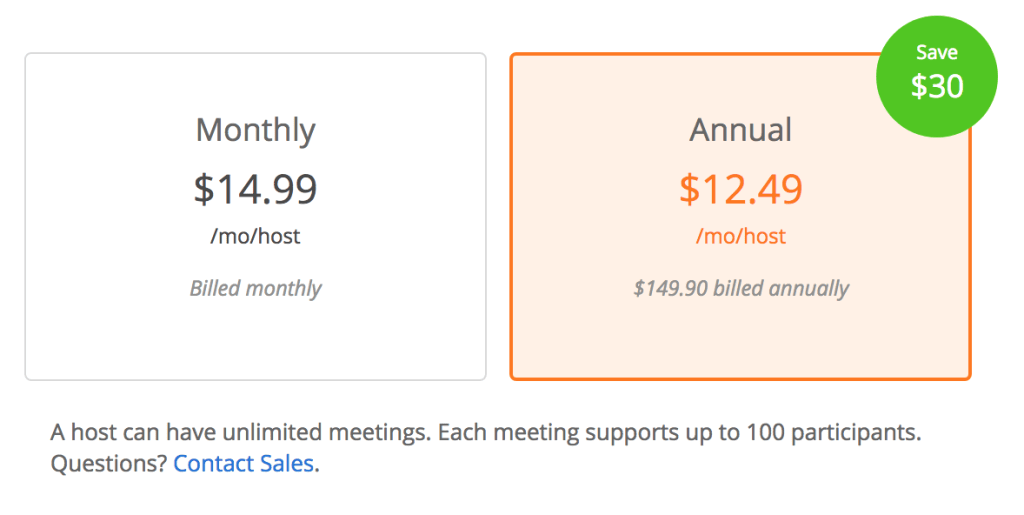
Anchoring Effect
The Anchoring Effect refers to the tendency to rely too heavily on the first fact they hear… whether it’s accurate or not, encountered when making decisions. This phenomenon is called anchoring.
The anchoring effect can help you or on the contrary — work against you. It’s one of the most important effects in cognitive psychology. When the anchoring effect helps you, it becomes easier to market your company’s products or services. If anchoring works against you, it’s difficult to change but you have to work on it.
In pricing strategies, anchoring involves presenting a higher-priced option first to make subsequent options seem more reasonable. This concept can influence perceptions of value and drive purchasing decisions.
Goal Gradient Effect
The Goal Gradient Effect suggests that people accelerate their efforts as they progress toward a goal.
This principle and tactic creates loyal customers. The good news is that it’s difficult to lose the loyal customers once you gain them. Loyalty programs, with their tiered rewards and points systems, tap into this concept, encouraging customers to continue engaging with a brand to attain the next level of benefits.
Let’s see some ways that can help you:
Step by step: Start with small requests (e.g., filling out contact forms) before asking for bigger ones (e.g., referrals).
Freebies: When someone becomes familiar with a quality, valuable, and well-designed product/service, it’s hard to refuse after the trial ends.
Wishlists: Consumers become connected to items added to their wishlists and it becomes difficult for them to remove them and refuse from the purchase.
Home try-on: Consumers usually tend to keep products already delivered to them.

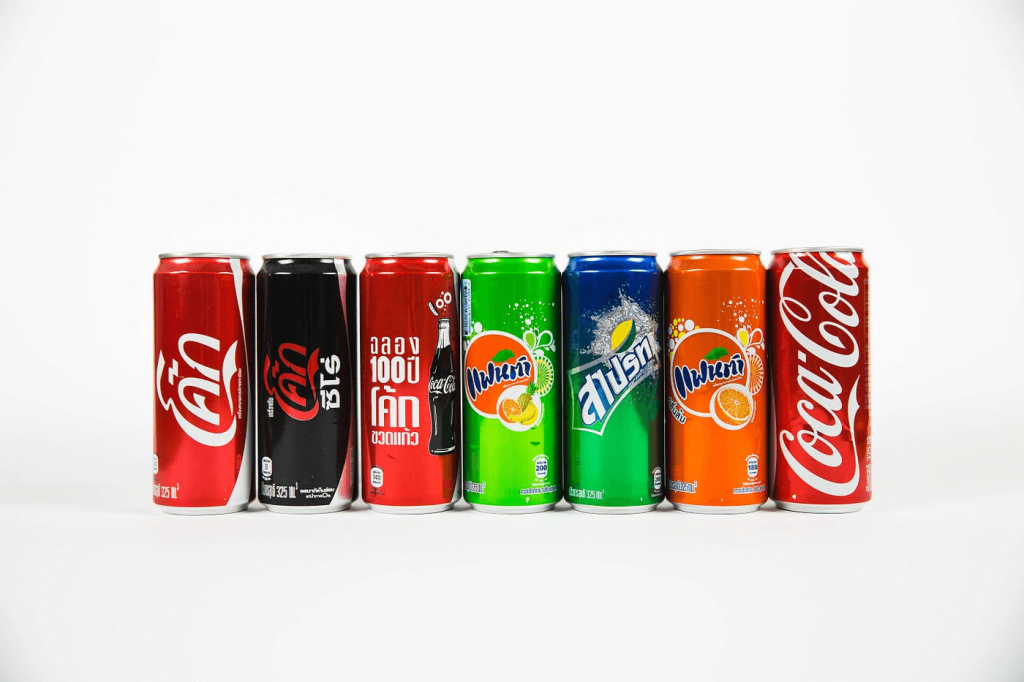
The Mere-Exposure Effect
The Mere-Exposure Effect means that people tend to prefer things merely because they are familiar with them.
Repetition of brand messaging, logos, and trials helps create familiarity. In turn, it makes consumers feel more comfortable and positively disposed towards a brand.

Authority Bias
Authority Bias involves giving greater weight to the opinions and actions of influencres. In marketing, leveraging expert endorsements, certifications, or affiliations can enhance a brand’s credibility and influence consumers to trust and choose the endorsed product or service.

Adapting Marketing Based on Psychology
To adapt marketing strategies based on psychology, consider the following approaches:
- Segmentation and Personalization
Tailor messages to specific audience segments, recognizing that different demographics may respond to psychological concepts differently.
- Emotional Appeal
Connect with consumers on an emotional level, as emotions often drive decision-making. Craft narratives that evoke positive emotions and align with consumers’ values.
- User-Generated Content
Leverage social proof by encouraging and showcasing user-generated content. This not only builds authenticity but also influences potential customers through the experiences of their peers.
- Transparency and Authenticity
Build trust by being transparent and authentic in marketing communications. Addressing potential concerns and presenting information honestly helps mitigate biases like skepticism and distrust.
- Dynamic Pricing Strategies
Understand the anchoring effect and experiment with dynamic pricing strategies. Presenting a higher-priced option first can influence how consumers perceive subsequent pricing tiers.
- Limited-Time Offers and Scarcity
Leverage the scarcity effect by incorporating limited-time offers and scarcity-driven promotions. Emphasize the exclusivity and urgency of these opportunities to encourage swift action.
- Influencer Collaborations
Use influencers strategically, taking advantage of the authority bias. Ensure influencers align with your brand values and are perceived as credible within your target market.
Wrapping Up
Psychology and marketing go side by side naturally, but there are techniques to use psychology intentionally to improve your marketing results. By incorporating and adapting strategies based on psychological principles, marketers can create campaigns that resonate with their target audience, influence decision-making processes, and ultimately drive success in the marketplace.
Focus on building quality products and earning the trust of your audience through responsible marketing strategies. It’s a strategy proven to work better in the long term. From the Halo Effect to the Authority Bias, each principle provides a unique lens through which marketers can decode the intricate tapestry of consumer behavior, guiding them toward more effective and impactful campaigns.
Is your business in need of a PR makeover?
- Benefit from media coverage assistance.
- Witness a refined branding approach.
- Watch as your recognition soars.





